What the Recent Report from UNCTAD Tells Us–And Why You Should Care
- Joonsup Yoon

- Jan 18
- 2 min read
Maritime has been a cornerstone of economic development for millennia, dating back to some 300,000 years ago when the first traders traveled to nearby regions on wooden caravans and ships.
Now our role on the sea has vastly expanded, with maritime freight taking up 70% of all transportation for trade worldwide. However, this also means one small disruption in the global supply chain could break out into a domino of disasters, imposing dire consequences on the global economy. And based on the recent report presented by the United Nations Trade & Development (UNCTAD), this may already be happening in our global seas.
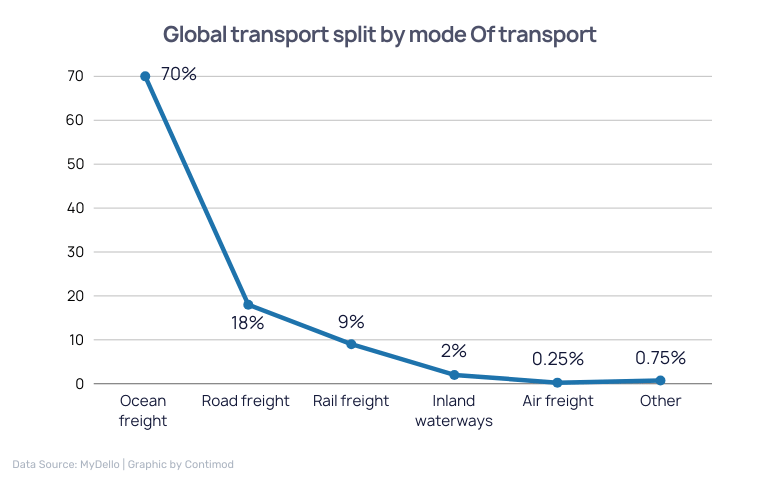
The UNCTAD produces annual reports detailing structural and cyclical changes affecting seaborne trade, ports and shipping, as well as an extensive collection of statistics ranging all the way back to 1968 on maritime transportation. And the most recent one, “Review of maritime transport 2024: Navigating maritime chokepoints,” has revealed fundamental problems in global logistics that influence our day-to-day.
One of the most startling chapters in this report involves concurrent disruptions in the Panama Canal, the Red Sea and the Suez Canal’s trade patterns. According to UNCTAD, the geopolitical tensions and global warming in maritime checkpoints (critical points along transport routes that facilitate the passage of substantial trade volumes which serve as vital arteries for global commerce, connecting important regions worldwide) force many ships to reroute or wait endlessly behind the gates, with a container ship with $10 billion worth of goods rendered immobile for six days due to blocking of the Suez Canal.
Changing trade patterns are also seen in Brazil and the United States’ expanding role as a grain exporter, surpassing Ukraine, which has been struck with a loss of 1.5 Billion dollars due to the continued conflict in Russian-Ukrainian conflict.
Environmental factors also cannot be overlooked. Türkiye (formerly known as Turkey) has recently imposed maritime regulations due to environmental concerns and traffic management, imposing additional stress on the maritime transportation. As for the Panama Canal, much of its water has been vaporized by global warming, and authorities have reduced the number of ships allowed to transit by 19.2% since 2023. While the rainy season in the region and efforts by the associated authorities has gradually increased the amount of ships transiting through the canal, this may be just a temporary alleviation.
The disruption of global supply chains affects everything around us, from fuel for your Honda to wheat for your favorite sourdough bread. As highschoolers, we must learn how to be weary about where our money is going. Are the companies that we consume from eco-friendly? What role do they play in prominent conflicts that influence maritime trade? These are questions that we can ask ourselves to make decisions that will help protect our planet from further damage and slowly reduce the stress on these maritime deliveries and heighten our living standards. Our actions no longer impact the country we live in, it impacts the world we too often take for granted.

Comments